The ISO21500 quality subject area contains three processes.
| ISO21500 process groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initiating | Planning | Implementing | Controlling | Closing | |
Quality | 4.3.32 Plan quality
| 4.3.33 Perform quality assurance | 4.3.34 Perform quality control
| ||
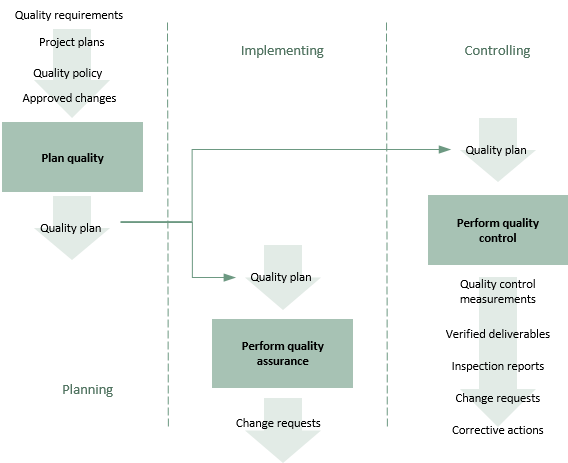
In the diagram below, these processes are presented as a flow diagram using the inputs and outputs defined in ISO21500. There is one planning, one implementing and one controlling process, in accordance with the three elements of quality management.
Click on the diagram for more detail on each process.
Praxis does not have a separate quality management function. Instead, it takes shares the view with ISO10006 that quality is implicit in all project and programme functions. The purpose of a project or programme is to produce outputs and outcomes that are ‘fit for purpose’, i.e. all elements of project and programme management are part of the delivery of a quality product.
That does not mean to say that quality planning, quality assurance and quality control are not explicitly mentioned with the framework, as explained below.
Praxis has two approaches to quality planning.
Firstly, the planning function will be applied to scope management to address quality of the outputs of the work.
Secondly, every functional procedure starts with a planning step that produces a management plan for that function.
The purpose of this process is to plan for quality. This means both the quality of the outputs produced and the quality of the processes used to manage the project or programme.
This process should establish with the sponsor and other stakeholders, what standards need to be achieved. It should also determine the tools, techniques, procedures and resources needed to achieve those standards. Any corporate policies for quality management are a key input to this process.
The output is a quality plan that also defines the type, timing and participants in quality reviews.
As with all ISO21500 subject area process groups, this is an iterative process which will be repeated each time changes are approved.
4.3.33 Perform quality assurance
The assurance function in Praxis is the equivalent of this process.
In simple terms, the job of quality assurance is to ensure that the quality plan is implemented. Some quality assurance is performed ‘internally’, i.e. the management team checks its own processes and outputs to ensure they meet the required standards.
It is also advisable that external assurance is performed, i.e. someone who is not part of the management team performs an audit to ensure that the quality plans are being implemented.
4.3.34 Perform quality control
In Praxis, this is covered by the elements of the control function that apply to scope – but also bearing in mind that in a broader sense quality may also depend upon other factors such as timeliness of delivery.
Quality control focuses on the quality of the outputs of the project or programme. This will involve pre-defined methods for testing outputs and will vary greatly according to the nature of the work being performed.
This process will establish whether outputs meet the required standards, analyse the cause of defects and determine corrective or future preventative action.
It is important that all test data and reports based on this data are recorded and communicated to interested parties.





