The term 'value' is often used to denote monetary value, but it means much more than that. Tucked away in corners of your home will be all sorts of mementoes and prized possessions that have little monetary value but have are of great value to you.
The term 'value' is often used to denote monetary value, but it means much more than that. Tucked away in corners of your home will be all sorts of mementoes and prized possessions that have little monetary value but have are of great value to you.
Terms such as 'sentimental value' show that something can have a value associated with it that has nothing to do with cash.
A key principle here is that value is subjective. Something can be of great value to me but of little value to you (a fact that we try to exploit in negotiation!). Value needs to be viewed from the point of view of the project stakeholders - but how does a stakeholder perceive value.
| Activity |
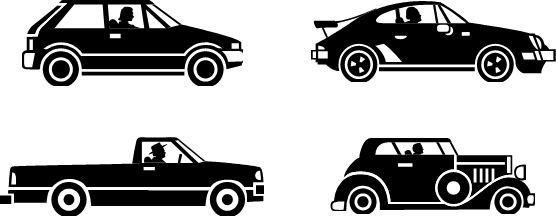
Value is in the eye of the beholder. Imagine you are buying a motor vehicle. Each of the vehicles shown below will get you from A to B so the decision must be based on more than that simple requirement. Make a note of the factors that may affect your choice between, a Family Saloon, a Sports Car, a Pickup Truck and a Classic Car? For example: seating capacity.
Click here to see a list we came up with. |
Value analysis identifies four different types of value:
- Cost value... is the total cost of producing the product.
- Use value... relates to the attributes of a product which enable it to perform its function.
- Esteem value... is the additional premium price which a product can attract because of its intrinsic attractiveness to purchasers.
- Exchange value... is the sum of the attributes which enable the product to be exchanged or sold.
Your list (and ours) contains perceptions of value that will be predominantly from the use category but you may have thought about esteem and exchange
In project terms, the cost value is the baseline cost of the product and is closely related to what earned value management assumes is the value of a product. This is an objective figure, albeit that it will be an estimate at the beginning of the project and only have a definite value on completion.
Use value is the key one for the business case. What financial return will we get from the product. This could take the form of sales income, efficiency savings and so on.
Esteem value is definitely subjective and very much dependent upon the user/buyer/observer of the product.
Exchange value may also be objective but will remain an estimate until the disposal of the product. This is only relevant if the business case covers whole life costing.
What next?
An example of the anlysis of value using a bicycle as an example. |